Neuron Network
Model
Contents
This model is built to select neurons which may have signal connections with AWA and AWB and to determine the specific promoters to express gene in them.
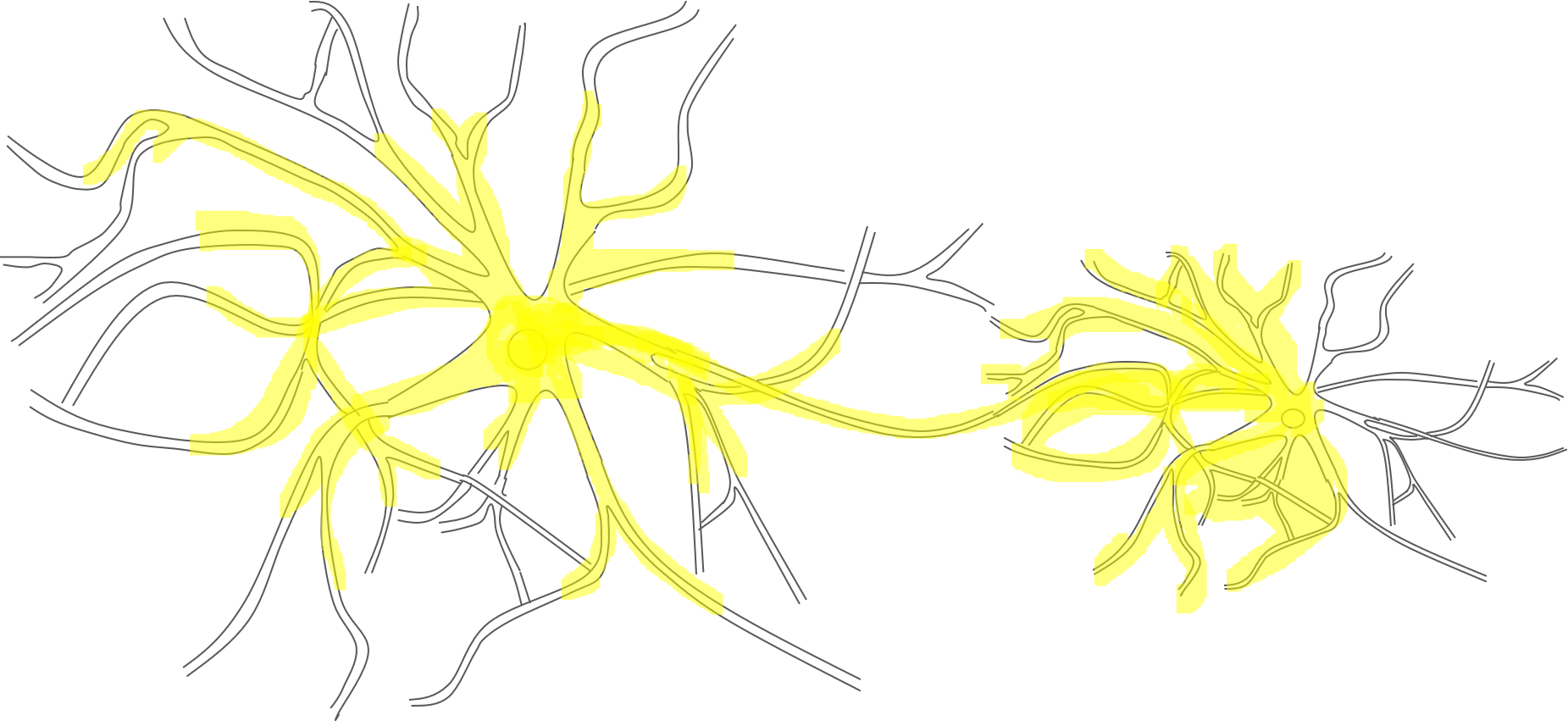
After we successfully integrated ord-10::CoChR::GEM-GECO::mCherry and str-1::Chrimson::GEM-GECO::GFP fusion genes in C. elegans(Caenorhabditis elegans) respectively, we can train worms by stimulating neurons AWA and AWB. After that, we hope to focus on the neuron network change due to new learning behaviors.
To achieve that, GEM-GECO, as calcium indicator, will also express in the downstream neurons of AWA AWB. We use our optical platform to receive the output signal of GEM-GECO when the neurons are activated. We expect to witness that for example, after worms are trained to be addicted with alcohol, the neuronal activation pattern surrounding the AWA AWB neuron will also change. New signal connection pathway may be built among neurons.
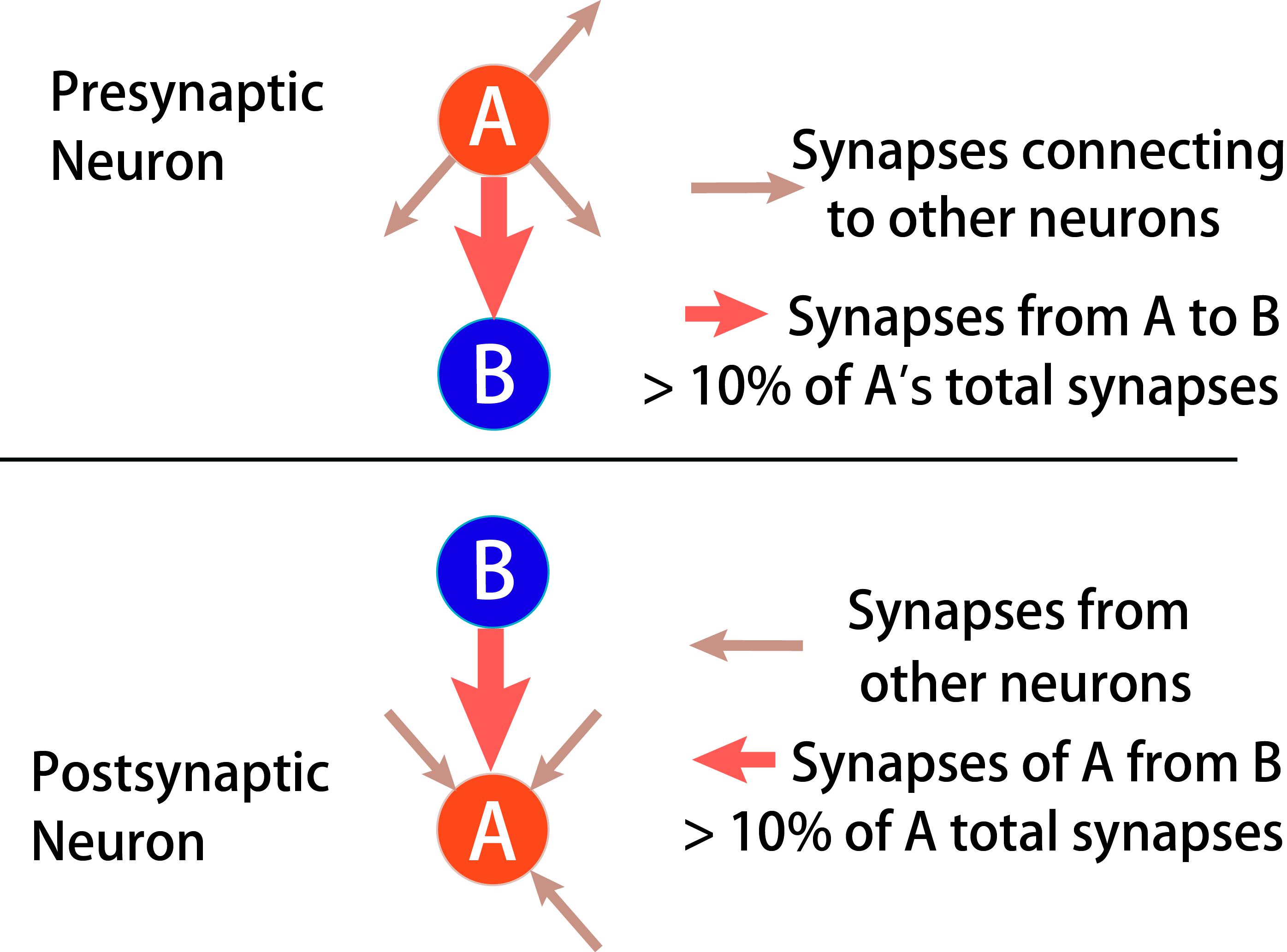
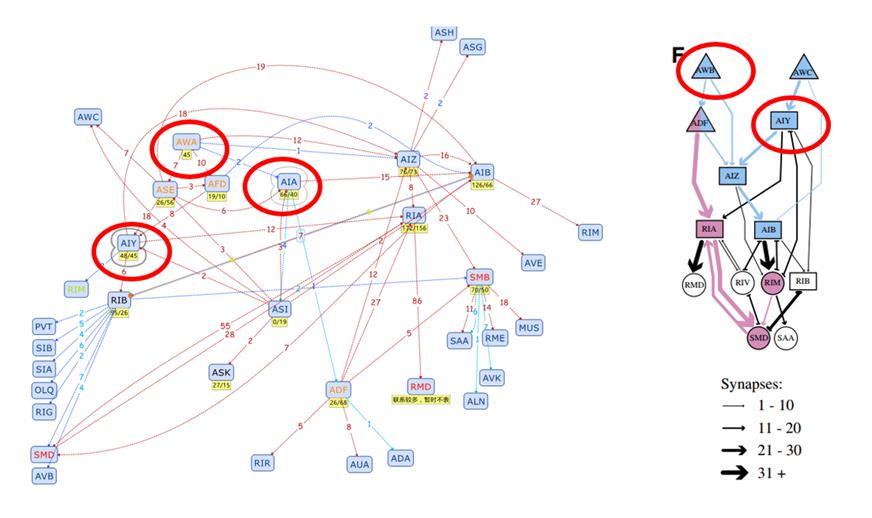
Firstly, we assume that the strength of a connection is positively correlated with the number of synapses, including synaptic outputs from any group of presynaptic neurons in the network should represent more than 10% of the total synaptic outputs of the presynaptic neurons and synaptic inputs to any group of postsynaptic neurons in the network should represent more than 10% of the synaptic inputs of the postsynaptic neurons.
2 steps are considered to design the further experiment:
- Select the neurons that are strongly connected with AWA AWB.
- Select specific promoters to express GEM-GECO in the neurons.
Determining the Connection Strength among Neurons
Firstly, we assume that the strength of a connection between neurons is positively correlated with the number of synapses. It includes synaptic outputs from any group of presynaptic neurons in the network should represent more than 10% of the total synaptic outputs of the presynaptic neurons and synaptic inputs to any group of postsynaptic neurons in the network should represent more than 10% of the synaptic inputs of the postsynaptic neurons(Figure 2.)[1].
Determining the Promoters
After getting a collection of potential downstream neurons, we need to determine which promoter to use. There are the basic requirements:
- The selected neurons cannot be too closed to each other. Thus we can distinguish each of them under microscope.
- AIA, AIY, AVA are the three neurons indicated to play important roles in worms movement [1,2,3], so they are prior to choose.
- The selected promoters should be as few as possible to express in neurons as many as possible.
Here are the work flow:
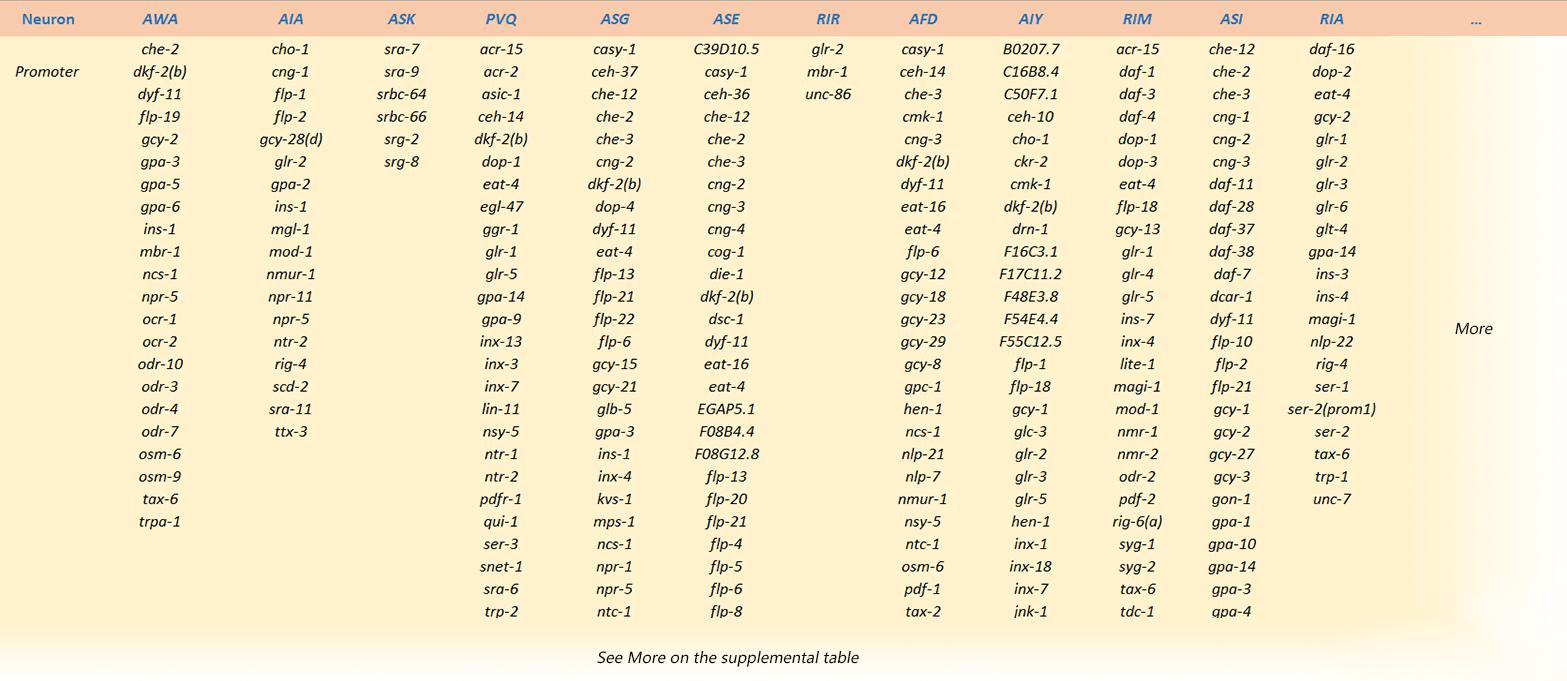
1.Make a table recording the promoter expression location. Data source. The table contains 43 neurons and their promoters
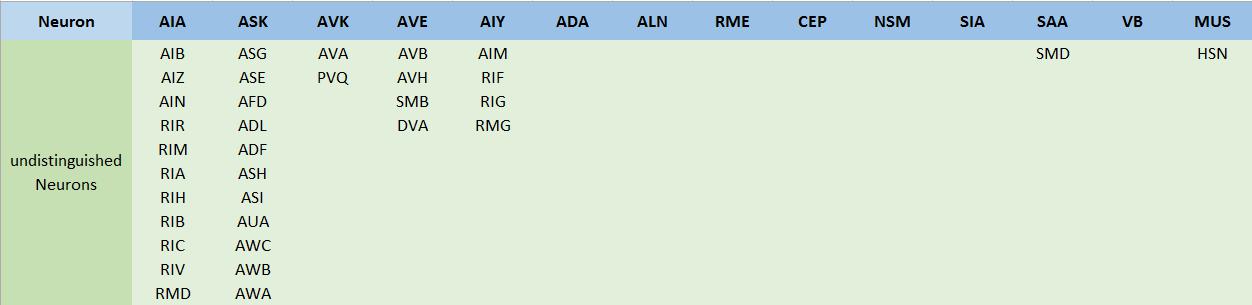
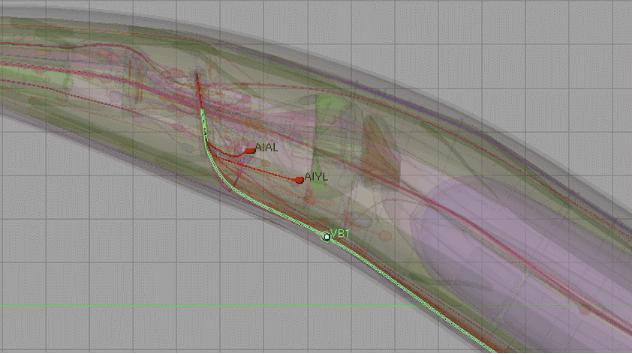
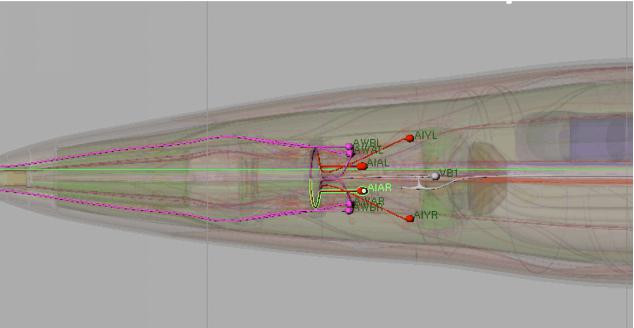
2.Make a table recording the neurons that cannot use the same promoter for they are close to each other. Data source. The table is manually made by evaluating the difficulty to distinguish neurons based on the online 3D model of C. elegans’ neurons (Figure 2.)
3.Write a MATLAB program to search the appropriate promoters based on the table2 and the requirement above 4.Remove the negative result based on table2 (in one column).
5.Print result in a text
Result:
According to our preference of neuron AIA,AIY,AVA, we selected two promoters: cho-1, unc-8.
cho-1 is expressed in AIA, AIY, VB
unc-8 is expressed in ASH, AVB, VB, AVA
Further work
We have constructed plasmids cho-1::GEM-GECO::GFP and unc-8::GEM-GECO::GFP. In the near future, we will demonstrate whether the neuronal connection among these neurons will change after worms get the newly learned behaviors.
References
- ↑ Ha, H., Hendricks, M., Shen, Y., Gabel, C. V., Fangyen, C., & Qin, Y., et al. (2010). Functional organization of a neural network for aversive olfactory learning in caenorhabditis elegans. Neuron, 68(6), 1173-86.